Have you ever wanted to try a new programming language but gave up because of all the prerequisites you need to install? Or did you want to make a small change in a (old) project only to find out that you need another version of the programming language than the one currently installed on your PC? With development containers (or dev containers), this can be something of the past.
According to the documentation, a dev container is a Docker container, setup to run an application or to sandbox tools, libraries, and/or runtimes needed for working with a codebase. The Visual Studio Code Remote - Containers extension makes it easy to setup a dev container and use it as a full-featured development environment.
Once setup, the configuration files (container definition) can be stored with the other project files in a version control system, so that whenever needed the same development environment can be re-created using the container definition.
Prerequisites
The following software must be installed to use dev containers:
- Docker Desktop
- Visual Studio Code
- Remote - Container VS Code extension
Setup a dev container for a new project
To setup a Python 3 dev container:
- Start Visual Studio Code
- Open the Command Palette with F1 or Ctrl + Shift + P
-
In the Command Palette, enter
remote containerand selectRemote Containers: Open Folder in Container...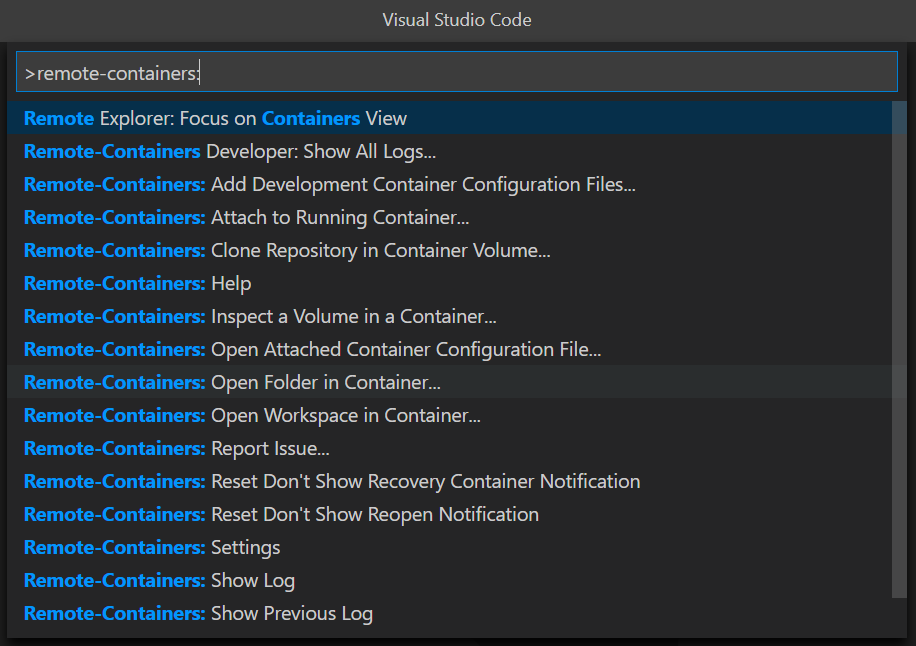
- In the Select Folder dialog, create a new folder for the Python project, select it and click Open
-
In the Add Development Container Configuration Files dialog, select
Show All Definitions...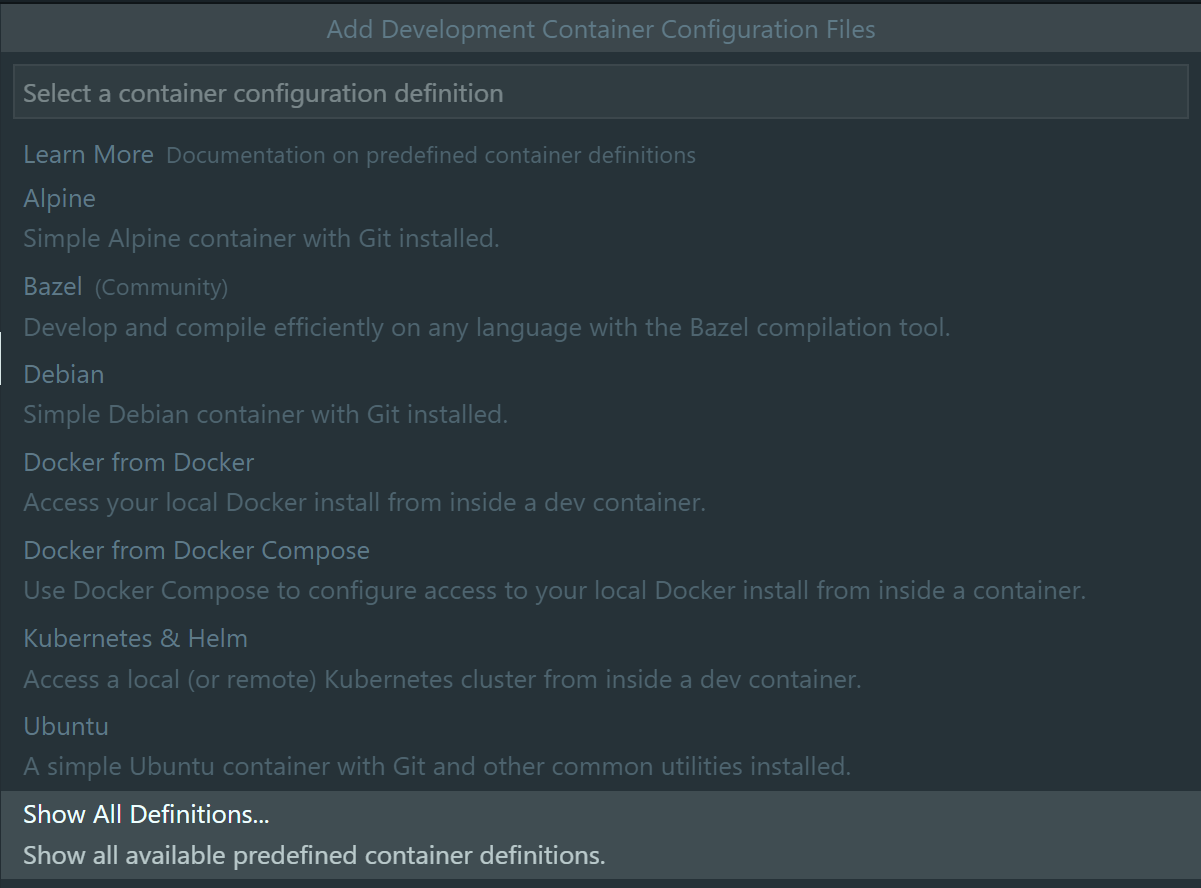
-
Enter
pand selectPython 3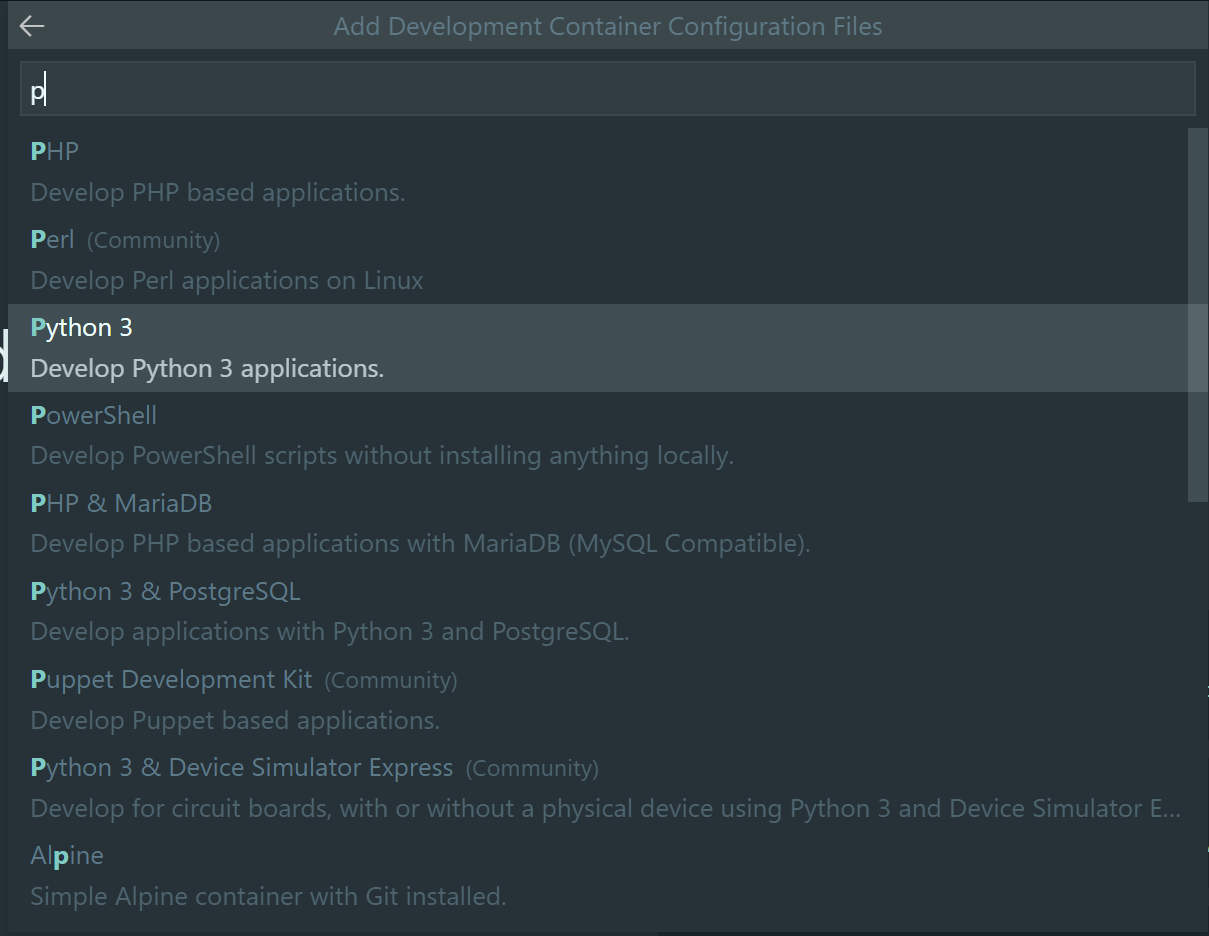
-
Select a
Python version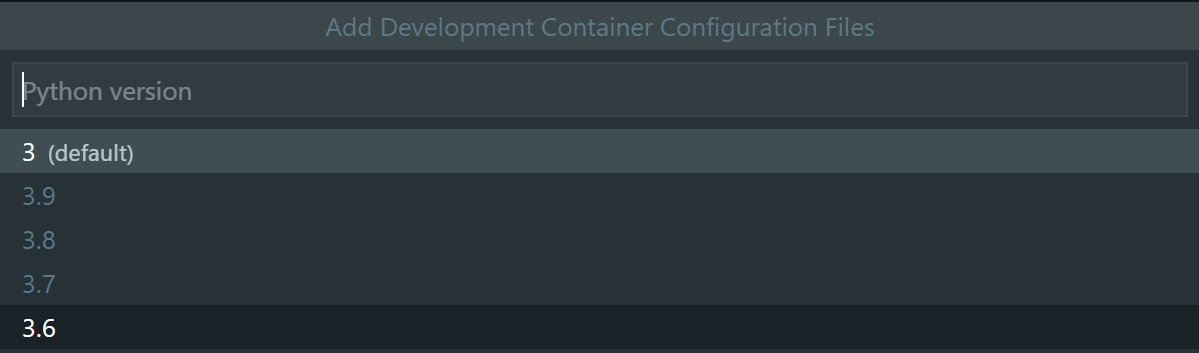
-
Select/Unselect
Python 3 dev container options. Click Ok to continue.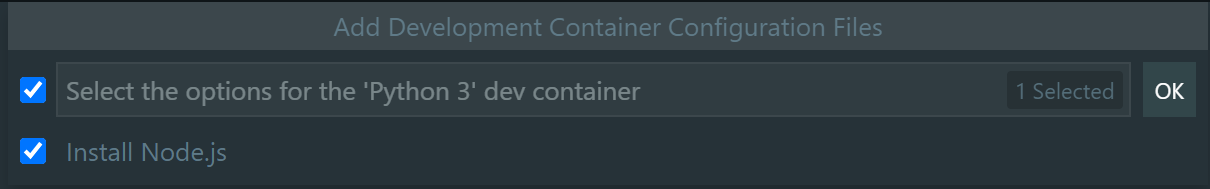
-
The following message will be displayed in the Remote Status bar item during the setup of the dev container

-
When the dev container setup is finished, the following message will be displayed in the Remote Status bar item

In theEXPLORERpane, there is a .devcontainer folder. The files in this folder contains the dev container definition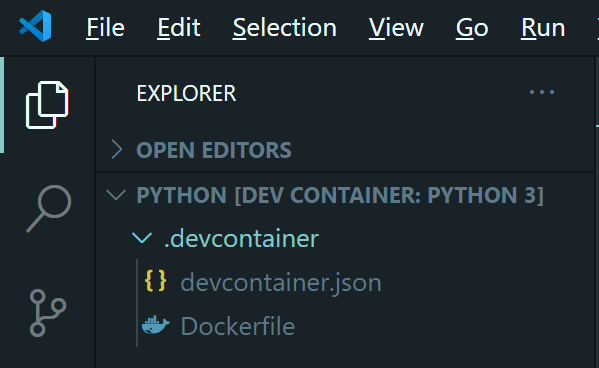
-
Open a terminal with Ctrl + \` and enter
python --versionto verify that you can run python code in the container
-
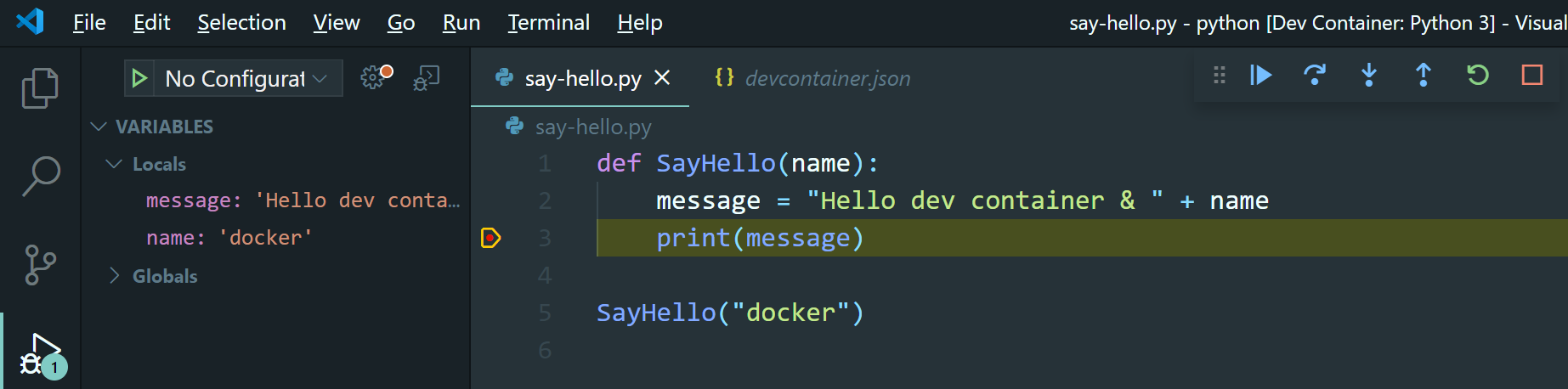
Create a Python module to test the debug and run functionality of Visual Studio Code
def SayHello(name): message = "Hello dev container & " + name print(message) SayHello("docker")Set a breakpoint on line 3 by clicking left of line 3. A red dot will then appear.
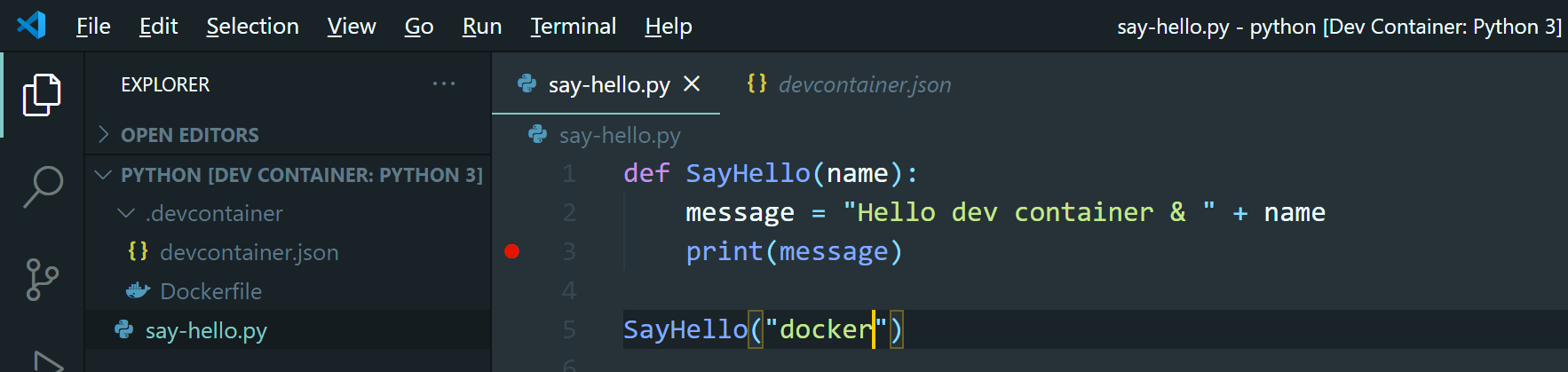
-
Press F5 and select
Python Filefrom the Select a debug configuration options to start a debug session.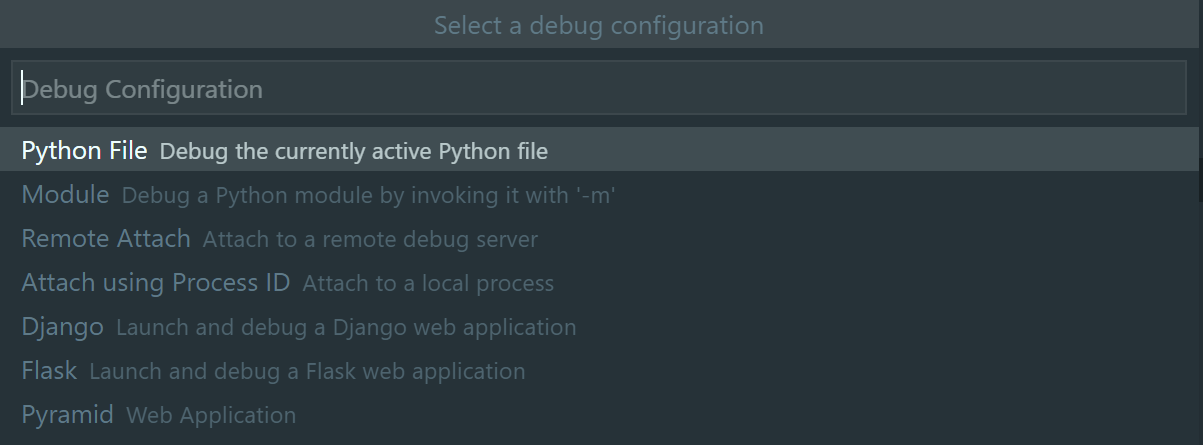
The debugger executes the module and stops at the breakpoint. In the variables panel, you can see the local variables and their value.
-
To stop and exit the dev container, click on the Remote Status bar item and select the
Close Remote Connectionoption from the Command palette.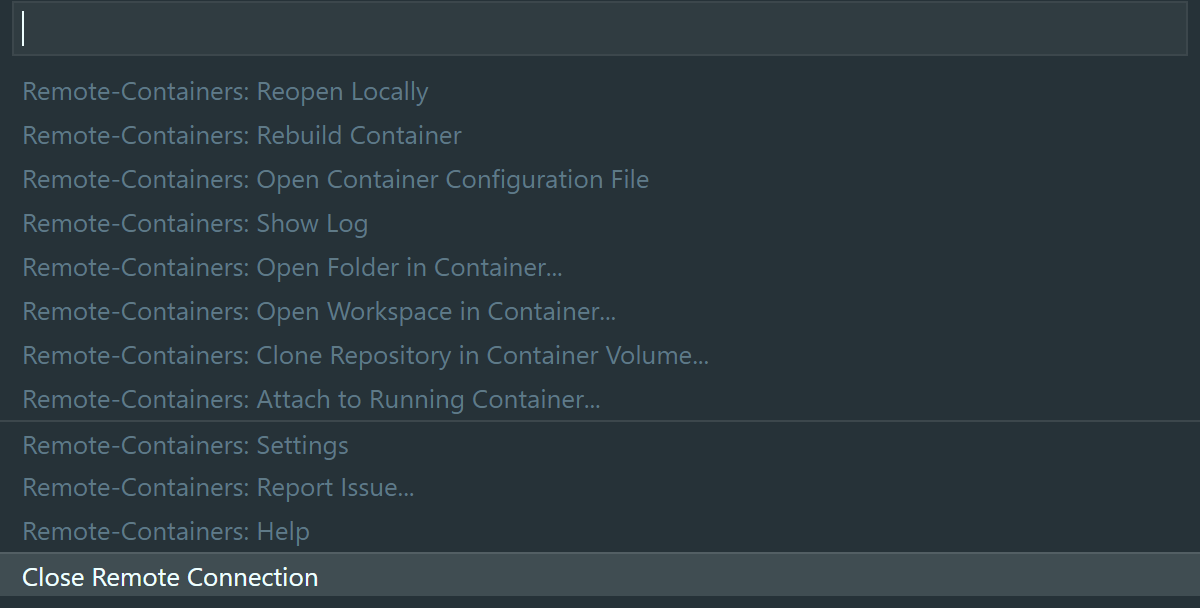
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to setup a dev container. There are a large number of predefined container definitions to select from. With dev containers, you can now setup isolated environments to experiment without the fear of polluting your PC.